To run:
modprobe snd_intel8x0m
slmodemd --alsa hw:1
modprobe snd_intel8x0m
slmodemd --alsa hw:1


function value = voltrade(S0,X,r,mu,t,sig,steps,NoPaths)Note, the above function will call some external functions that are not defined here. Anyway, the objective of the function is to generate Monte Carlo simulation of stock prices, and at each time step to find the corresponding call option price, and also then to find the return of portfolio based on longing one call option and shorting delta number of stock. The function parameters are : S0 (current stock price), X (call option exercise price), r (risk free rate), mu (expected stock return), t (time to maturity), sig (volatility of stock), steps (number of delta t), and NoPaths (number of paths for Monte Carlo simulation).
dt = t/steps;
drift = (mu - 0.5 * sig ^ 2) * dt;
vol = sig * sqrt(dt);
[price, delta, gamma] = tri_Eprice(S0, X, r, t, steps, sig, 0, 1);
Z = [zeros(NoPaths, 1) normrnd(drift, vol, NoPaths, steps)];
Z = (cumsum (Z'))';
S = S0*exp(Z);
ttm= [ones(NoPaths, steps) * dt];
ttm = cumsum (ttm')';
flipttm = [fliplr(ttm) (zeros(NoPaths, 1)+0.0000001)];
ttm = [(zeros(NoPaths, 1)+0.0000001) ttm];
callprice = blackscholes(S, X, r, flipttm, sig, 0) .* exp(-r.*ttm);
Sp = S .* exp(-r.*ttm);
value = mean(callprice - callprice(1,1) + (S0 - Sp) * delta);
subplot (2,1,1);
plot (value);
xlabel ('time step');
ylabel ('portfolio return');
subplot (2,1,2);
plot (mean(S));
xlabel ('time step');
ylabel ('stock price');
voltrade (50,50,0.05,0.3,0.5,0.4,1000,1000);The return of the portfolio would look as below:

voltrade (50,50,0.05,-0.3,0.5,0.4,1000,1000);The result:

voltrade (50,50,0.05,0.0,0.5,0.4,1000,1000);

X11Forwarding yesNow, you'll need to re-ssh to LM using Putty. Check the event log ensure that "X11 forwarding enabled" is there and on the terminal type echo $DISPLAY whether it's been set by Putty.
X11DisplayOffset 10
X11UseLocalhost yes
And, restart sshd
/etc/rc.d/rc.sshd restart

xrdb $HOME/.Xresources
xsetroot -solid grey
xterm -geometry 80x24+10+10 -ls -title "$VNCDESKTOP Desktop" &
twm &
This answer is actually a bad one, at least compared to Ariya's answer in the sense that the probability that a call to this function will generate the respective random number directly without involving the loop is really low. Huh ?!?!? Okay, basically let me say that the inner loop will generate hit 80 % of the time. Why? Because there are 5 possibilities, and 4 of them are used to generate discrete integer random number 1..10 while 1 is deliberately ignored. Meanwhile, the outer loop will obviously generate 70 % hit. So, in the end the code will be effective 56 % (as in 80 % x 70 %, right ?) of the time without involving any loop. Actually, I think Ariya's answers are some of the most efficient implementations possible, especially the first one, hehe. Had I seen the challenge earlier, I wouldn't have been able to generate an implementation of the same quality, it would be so so like the above :(.int r,x;
do{
do{
r = rand5();
if (r > 2 && r <= 4) x = rand5() + 5;else if (r <= 2) x = rand5();
}while (r > 4);
}while (x > 7);
return x;
function r = rand5(m,n)This code will generate a matrix of m row and n column of discrete random numbers. Let's see the code to generate rand7.
r = floor(5 * rand(m,n) + 1);
function r = rand7(n)The code above will generate a vector of n discrete random numbers 1..7.
m = 1000;
sig = sqrt(2);
mu = 3;
temp = sum(rand5(m,n));
zn = (temp - m * mu)/(sig * sqrt(m));
x=0.5*erfc(-zn/sqrt(2));
r = floor(mod(x*70,7))+1;


# The script is used to check whether harddrive load cycle count has increased by 90 cycles
# on a daily basis (24 hour)
# it doesn't run as a daemon
# to run : python hdcheck.py
# it will create 2 files:
# -timestamp.dat is used to check the delta time since the first run
# -lcc.dat is used to check the increase in load cycle count
# The next time you run it, it will check the current load cycle count and do the calculation
# To start anew delete those 2 files, and rerun
# GAH_2007
import re
import os
import time
import datetime
import cPickle
put, get = os.popen4("df")
dev = []
current_lcc = {}
for dfout in get.readlines():
p = re.compile("/dev/\w\w\w[1-9]")
m = p.match(dfout)
if m:
dev.append(m.group())
for ent in dev:
put, get = os.popen4 ("smartctl -a "+ent+ "| grep Load_Cycle_Count")
for smartctlout in get.readlines():
p = re.compile("\d*\n")
m = p.findall(smartctlout)
p = re.compile("\d*")
n = p.match(m[0])
if n:
current_lcc[ent] = n.group()
time = time.mktime(datetime.datetime.now().timetuple())/3600.0
delta_time = 0
try:
f = open ("timestamp.dat", "r")
timestamp = cPickle.load(f)
f.close()
delta_time = time - timestamp
except:
timestamp = 0
if (timestamp):
print "Time since the first run is", delta_time, "hour"
else:
try:
f = open ("timestamp.dat", "w")
cPickle.dump(time, f)
f.close()
except:
print "unable to save timestamp"
try:
f = open ("lcc.dat", "r")
previous_lcc = cPickle.load(f)
f.close()
lcc_increase = {}
except:
previous_lcc = 0
if (previous_lcc):
for dev in current_lcc.keys():
lcc_increase[dev] = eval(current_lcc[dev]) - eval(previous_lcc[dev])
else:
try:
f = open ("lcc.dat", "w")
cPickle.dump(current_lcc, f)
f.close()
except:
print "unable to save current load cycle count data"
if (timestamp and previous_lcc):
for dev in current_lcc.keys():
lcc_increase_daily = lcc_increase[dev] * 24.0 / delta_time
print dev + " load cycle count increases by "+ str(lcc_increase[dev])+ " cycles("+str(lcc_increase_daily)+" on daily basis)"
if (lcc_increase_daily > 90):
print " Load cycle count increase by more than 90 !!"
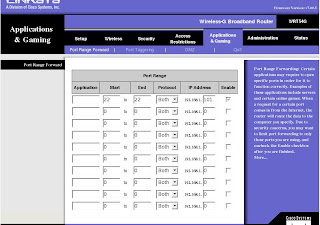
tar zxvf prex-0.5.0.tar.gzIt will generate an image file 'prexos' in the current directory. The image file is not bootable by qemu. In order to run it via qemu, we have to make use the available floppy image, and replace it with the latest version. Basically, the image file consists of bootsector.bin which is located in the first sector and the prexos image in the root directory. Meaning, we have to replace the prexos image from the latest stable 0.3.0 with the recently compiled 0.5.0.
cd prex-0.5.0/
./configure --target=i386-pc
make
kedit /etc/mtools.conf &Replace
drive a: file="/dev/fd0" exclusivewith
drive a: file="[directory of the floppy image]/prex -0.3.0.i386-pc.img" exclusive
type o (overwrite).cd prex-0.5.0/
mcopy prexos a:
Long file name "prexos" already exists.
a)utorename A)utorename-all r)ename R)ename-all o)verwrite O)verwrite-all
s)kip S)kip-all q)uit (aArRoOsSq):
qemu -fda prex-0.3.0.i386-pc.imgHere's a screenshot:

makeThen, we need to make a configuration file, /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf. The entry of the file as provided by http://opensource.nus.edu.sg/wiki/index.php/Connecting_to_PEAP_in_NUS and here:
cp wpa_cli wpa_supplicant /usr/local/bin
ctrl_interface=/var/run/wpa_supplicantThe content of ase1.pem is as such :
network={
ssid="NUS"
scan_ssid=1
key_mgmt=IEEE8021X
eap=PEAP
ca_cert=”/etc/cert/ase1.pem”
phase2=”auth=MSCHAPV2”
}
Then, run the wpa_supplicant using :-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDJzCCApCgAwIBAgIBATANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQQFADCBzjELMAkGA1UEBhMCWkEx
FTATBgNVBAgTDFdlc3Rlcm4gQ2FwZTESMBAGA1UEBxMJQ2FwZSBUb3duMR0wGwYD
VQQKExRUaGF3dGUgQ29uc3VsdGluZyBjYzEoMCYGA1UECxMfQ2VydGlmaWNhdGlv
biBTZXJ2aWNlcyBEaXZpc2lvbjEhMB8GA1UEAxMYVGhhd3RlIFByZW1pdW0gU2Vy
dmVyIENBMSgwJgYJKoZIhvcNAQkBFhlwcmVtaXVtLXNlcnZlckB0aGF3dGUuY29t
MB4XDTk2MDgwMTAwMDAwMFoXDTIwMTIzMTIzNTk1OVowgc4xCzAJBgNVBAYTAlpB
MRUwEwYDVQQIEwxXZXN0ZXJuIENhcGUxEjAQBgNVBAcTCUNhcGUgVG93bjEdMBsG
A1UEChMUVGhhd3RlIENvbnN1bHRpbmcgY2MxKDAmBgNVBAsTH0NlcnRpZmljYXRp
b24gU2VydmljZXMgRGl2aXNpb24xITAfBgNVBAMTGFRoYXd0ZSBQcmVtaXVtIFNl
cnZlciBDQTEoMCYGCSqGSIb3DQEJARYZcHJlbWl1bS1zZXJ2ZXJAdGhhd3RlLmNv
bTCBnzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOBjQAwgYkCgYEA0jY2aovXwlue2oFBYo847kkE
VdbQ7xwblRZH7xhINTpS9CtqBo87L+pW46+GjZ4X9560ZXUCTe/LCaIhUdib0GfQ
ug2SBhRz1JPLlyoAnFxODLz6FVL88kRu2hFKbgifLy3j+ao6hnO2RlNYyIkFvYMR
uHM/qgeN9EJN50CdHDcCAwEAAaMTMBEwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zANBgkqhkiG
9w0BAQQFAAOBgQAmSCwWwlj66BZ0DKqqX1Q/8tfJeGBeXm43YyJ3Nn6yF8Q0ufUI
hfzJATj/Tb7yFkJD57taRvvBxhEf8UqwKEbJw8RCfbz6q1lu1bdRiBHjpIUZa4JM
pAwSremkrj/xw0llmozFyD4lt5SZu5IycQfwhl7tUCemDaYj+bvLpgcUQg==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
wpa_supplicant -i eth1 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf -BMight want to try using -Dwext or -Dipw (deprecated)
wpa_gui &Obtain ip address using:
dhclient eth1To connect to NUSOPEN (NUS open network), set the essid to NUSOPEN:
iwconfig eth1 essid "NUSOPEN"then obtain the ip address using dhclient as before (or dhcpcd eth1).
cd /usr/src/linuxUnder "Power management options (ACPI, APM)" tab, check whether "suspend to RAM and standby" exists. If it doesn't, I suppose suspend is not supported by your kernel.
make xconfig
echo -n "mem" > /sys/power/statePress Fn button on your thinkpad to resume.
cd /bootIt will create /boot/initrd.tgz file, that we'll want to load it along with the kernel at boot time. Now edit the /etc/lilo.conf :
mkinitrd -c -k 2.6.23-smp -m ext3 -f ext3 -r /dev/hda2
kedit /etc/lilo.confThe linux part should look like this :
image = /boot/vmlinuzThen, run lilo and reboot to check whether it works.
initrd = /boot/initrd.gz
root = /dev/hda2
label = newLinux
read-only
image = /boot/vmlinuz-huge-smp-2.6.21.5-smp
root = /dev/hda2
label = oldLinux
read-only
Basically, acpid just executes scripts residing inThen reboot, to restart the acpi daemon./etc/acpi/actions. Which script to launch at which event is configured in several files in/etc/acpi/events. All actions are documented in/var/log/acpid.
The event script needs to be created within/etc/acpi/eventsand can have any name you like. In this case we call it lid because it will trigger the lid event. Do# vi /etc/acpi/events/lidand make it look like this:event=button/lid
action=/etc/acpi/actions/sleep.sh %eThe "event" line is a regular expression specifying the events we're interested in. You can determine what the event strings are from looking at
The "action" line is the command to be executed when these events are dispatched. In this example we call the/var/log/acpidafter trying to suspend, close the lid, etc. . You can find information about the event strings ibm-acpi generates for certain keys at the Special Keys HOWTO.sleep.shscript residing in/etc/acpi/actionsand pass the event description text using the %e placeholder.
Our example/etc/acpi/actions/sleep.shscript looks as follows:#!/bin/sh
# if launched through a lid event and lid is open, do nothing
echo "$1" | grep "button/lid" && grep -q open /proc/acpi/button/lid/LID/state && exit 0
# remove USB 1.1 driver
rmmod uhci_hcd
# sync filesystem and clock
sync
/sbin/hwclock --systohc
# switch to console
FGCONSOLE=`fgconsole`
chvt 6
/usr/sbin/radeontool light off
# go to sleep
sleep 5 && echo -n "mem" > /sys/power/state
# readjust the clock (it might be off a bit after suspend)
/sbin/hwclock --adjust
/sbin/hwclock --hctosys
# reload USB 1.1 driver
modprobe uhci_hcd
# turn on the backlight and switch back to X
radeontool light on
chvt $FGCONSOLE
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libntfs.so.10 libntfs.so.10Then in /etc/fstab, add:
ln -s /usr/local/lib/libfuse.so.2 libfuse.so.2
setenv KDEWM blackbox
SopCast client version 1.0.2 library dependencyThen, from konsole:
If you don't have stdc++ 5 in your system, please download the libstdcpp5.tgz from
www.sopcast.com, and copy the
libstdc++.so.5
libstdc++.so.5.0.1
to /usr/lib/
The copy command must be:
cp -a libstdc++.so.5* /usr/lib
With '-a' parameter, and you must login as root.
1. sp-sc-auth
A simple example of sp-sc command line.
./sp-sc-auth sop://broker.sopcast.com:3912/6098 3908 8908 > /dev/null &
Start to transfer channel 6098, and you can play it on 8908 with VLC or mplayer
by open the url: http://localhost:8908/tv.asf
mplayer -zoom http://localhost:8908/tv.asfWhat's interesting from the Linux version of vlc is that here we could stream several channels at the same time, which is not possible in that of Windows XP's.
Start streaming channel 1(Channel ID:6001, Port: 8908)
./sp-sc-auth sop://broker.sopcast.com:3912/6001 3908 8908 > /dev/null &
Show the channel at mplayer:
mplayer http://localhost:8908/tv.asf
Start streaming channel 2:(Channel ID:6002, Port 8909)
./sp-sc-auth sop://broker.sopcast.com:3912/6002 3908 8909 > /dev/null &
Show the channel at mplayer: (Note, now the TCP port is 8909)
mplayer http://localhost:8909/tv.asf
etc
#!/bin/bash
cd /usr/lib/python2.5/idlelib/
python PyShell.py &
cd ~
First download the slackbuild script here.
Untar it.
Download the source from here.
Copy the source the the slackbuild directory:
cp OOo_2.3.0_LinuxIntel_install_en-US.tar.gz openoffice.org
Make the script executable:
chmod +x openoffice.org.SlackBuild
./openoffice.org.SlackBuild
When done creating the package, install it with installpkg:
cd /tmp
installpkg openoffice.org-2.3.0_en_US-i586-1_SBo.tgz
modprobe usb-storageSlocate: It provides a secure way to index and quickly search for all files on
cd /mnt
mkdir usbflash
nano /etc/fstab
add: /dev/sda1 /mnt/usbflash vfat,ntfs noauto,owner,user,umask=0 0 0
The sda1 represents the device name that the kernel gives the USB flash when it gets plugged in.
mount /mnt/usbflash
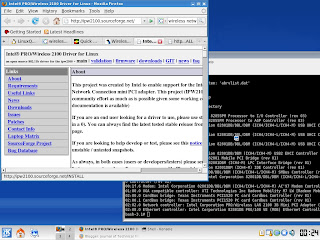
slocate -uWireless LAN: Based on /sbin/lspci, the driver for the system (IBM Thinkpad T40) is Intel Corporation PRO/Wireless LAN 2100 3B Mini PCI Adapter. After searching the net, I've got these results: http://ipw2100.sourceforge.net/, http://jrblevin.freeshell.org/linux/ipw2100/, http://ipw2100.sourceforge.net/. According to the installation manual , starting with Linux kernel version 2.6.14, an old stable version of the Intel PRO/Wireless 2100 Network Connection driver is provided in the kernel. All we need to do is to download the firmware from http://ipw2100.sf.net/firmware.php , untar it, and copy all the files to /lib/firmware. The specific files are :
slocate
ipw2100-(version number).fw Boot strap imageLoad the module with:
ipw2100-(version number)-i.fw Used in IBSS mode
ipw2100-(version number)-p.fw Used in monitor mode
modprobe ipw2100check the output of dmesg to see if it is successful:
dmesg | tailSlackpkg: is a tool to install or upgrade Slackware official packages from a mirror.
Download the tarball2. Adobe Reader
tar zxvf install_flash_player_9_linux.tar.gz
cd install_flash_player_9_linux/
cp libflashplayer.so ~/usr/lib/mozilla/plugins/
cp flashplayer.xpt ~/usr/lib/firefox-2.0.0.4/components/
Download the tarball3. JRE
tar zxvf AdobeReader_enu-7.0.9-1.i386.tar.gz
cd AdobeReader
./INSTALL
all the files are installed at /usr/local/Adobe/Acrobat7.0/
acroread
expr: syntax error message shows, to work it out :
nano /usr/local/Adobe/Acrobat7.0/
comment the line : check_gtk_ver_and_set_lib_path "$MIN_GTK_VERSION"
i.e. # check_gtk_ver_and_set_lib_path "$MIN_GTK_VERSION"
The Slackware package can be found from the slackware stable repository
http://plugindoc.mozdev.org/faqs/java.html#Linux
ln -s /usr/lib/jre1.6.0_02/plugin/i386/ns7/libjavaplugin_oji.so /usr/lib/mozilla/libjavaplugin_oji.so

import random
import math
price = 33
exercise = 30
expiry = 6.0
vol = 9.0/100
rate = 5.0/100
simNum = 5000000
mean = math.log (price) + (rate - vol * vol / 2) * expiry / 12.0
stddev = math.sqrt(vol * vol * expiry / 12.0)
sum = 0
for i in range (simNum):
ft = math.exp(random.normalvariate(mean,stddev)) - exercise
if (ft <= 0): ft = 0 sum = sum + ft average = sum / simNum optionsPrice = average * math.exp(-rate*expiry/12.0) print "The options price based on " + str(simNum) + " observations is " + str(optionsPrice)